LeetCode day6
125. Valid Palindrome
Topic: String, Two pointer
Given a string, determine if it is a palindrome, considering only alphanumeric characters and ignoring cases.
Note: For the purpose of this problem, we define empty string as valid palindrome.
Example 1:
Input: "A man, a plan, a canal: Panama"
Output: trueExample 2:
Input: "race a car"
Output: falseApproach1
my sol
def isPalindrome(s: str) -> bool:
s = s.lower()
s = s.translate(str.maketrans('', '', string.punctuation))
s = s.replace(' ', '')
# print(s)
i,j = 0,len(s)-1
while j >= i:
# print(s[i],s[j])
if s[i] == s[j]:
i += 1
j -= 1
else:
return False
return TrueApproach2
re, faster
def isPalindrome(s: str) -> bool:
#p=''.join(re.findall(r'[\w\d]+',s))
p=''.join(re.findall(r'[a-zA-Z0-9]+',s))
p=p.lower()
return True if p==p[::-1] else False136. Single Number
Topic: Bit manipulation, Hash Table
Given a non-empty array of integers, every element appears twice except for one. Find that single one.
Note:
Your algorithm should have a linear runtime complexity. Could you implement it without using extra memory?
Example 1:
Input: [2,2,1]
Output: 1Example 2:
Input: [4,1,2,1,2]
Output: 4Approach1
brute force (over time)
def singleNumber(nums: List[int]) -> int:
for i in range(len(nums)):
for j in range(len(nums)):
if i != j:
if nums[i] == nums[j]:
break
# 这里只有不break才会触发
else:
return nums[i]Approach2
Counter
from collections import Counter
def singleNumber(nums: List[int]) -> int:
datas = Counter(nums)
for each in datas:
if datas[each] == 1:
return eachApproach3
By math (Smart)
def singleNumber(nums):
return 2 * sum(set(nums)) - sum(nums)先通过set把数据去重,然后把所有的值相加*2去减之前的值,剩下的值就是答案
Approach4
XOR
- 0和任何数异或的结果是这个任何数
任何相同的数异或的结果是0
def singleNumber(nums): a = 0 for i in nums: a ^= i return a
141. Linked List Cycle
Topic: Linked list, Two pointer
Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it.
To represent a cycle in the given linked list, we use an integer pos which represents the position (0-indexed) in the linked list where tail connects to. If pos is -1, then there is no cycle in the linked list.
Example 1:
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
Output: true
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the second node.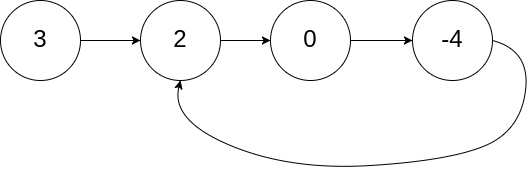
Example 2:
Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
Output: true
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the first node.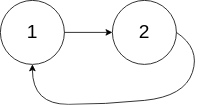
Example 3:
Input: head = [1], pos = -1
Output: false
Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.
Approach1
Hash 空间复杂度O(n). 把遍历过的节点记录,当发现遍历的节点下一个节点遍历过, 说明有环
def hasCycle(head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: bool
"""
lookup = set()
p = head
while p:
lookup.add(p)
if p.next in lookup:
return True
p = p.next
return FalseApproach2
快慢指针, 空间复杂度O(1); 好像两个人在一个操场上跑步,速度快的人一定会和速度慢的相遇(环) (可能会多跑几圈)
def hasCycle(head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: bool
"""
slow = head
fast = head
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next # 它跑一步
fast = fast.next.next # 它跑两部
if slow == fast:
return True
return False155. Min Stack
Topic: Design, Stack
Design a stack that supports push, pop, top, and retrieving the minimum element in constant time.
- push(x) – Push element x onto stack.
- pop() – Removes the element on top of the stack.
- top() – Get the top element.
- getMin() – Retrieve the minimum element in the stack.
Example 1:
Input
["MinStack","push","push","push","getMin","pop","top","getMin"]
[[],[-2],[0],[-3],[],[],[],[]]
Output
[null,null,null,null,-3,null,0,-2]
Explanation
MinStack minStack = new MinStack();
minStack.push(-2);
minStack.push(0);
minStack.push(-3);
minStack.getMin(); // return -3
minStack.pop();
minStack.top(); // return 0
minStack.getMin(); // return -2Approach1
my
class MinStack:
def __init__(self):
"""
initialize your data structure here.
"""
self.stack = []
def push(self, x: int) -> None:
self.stack.append(x)
def pop(self) -> None:
self.stack.pop()
def top(self) -> int:
return self.stack[-1]
def getMin(self) -> int:
return min(self.stack)Approach2
最小栈
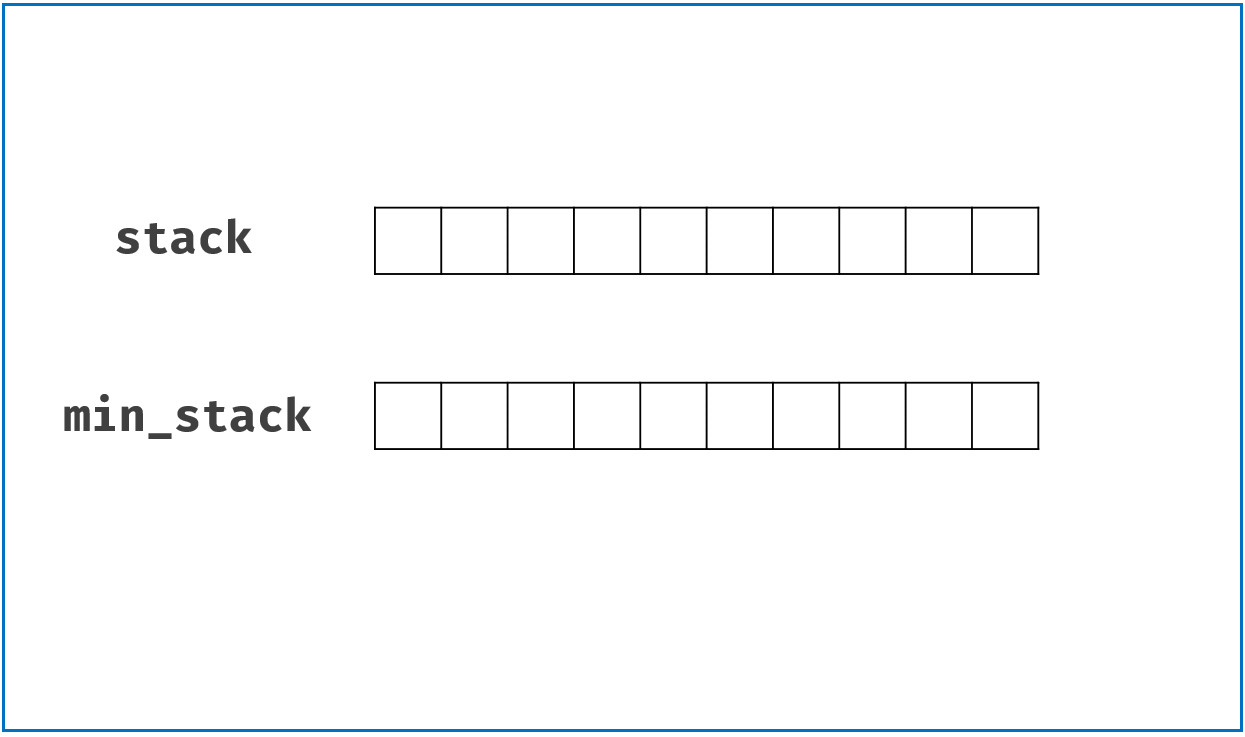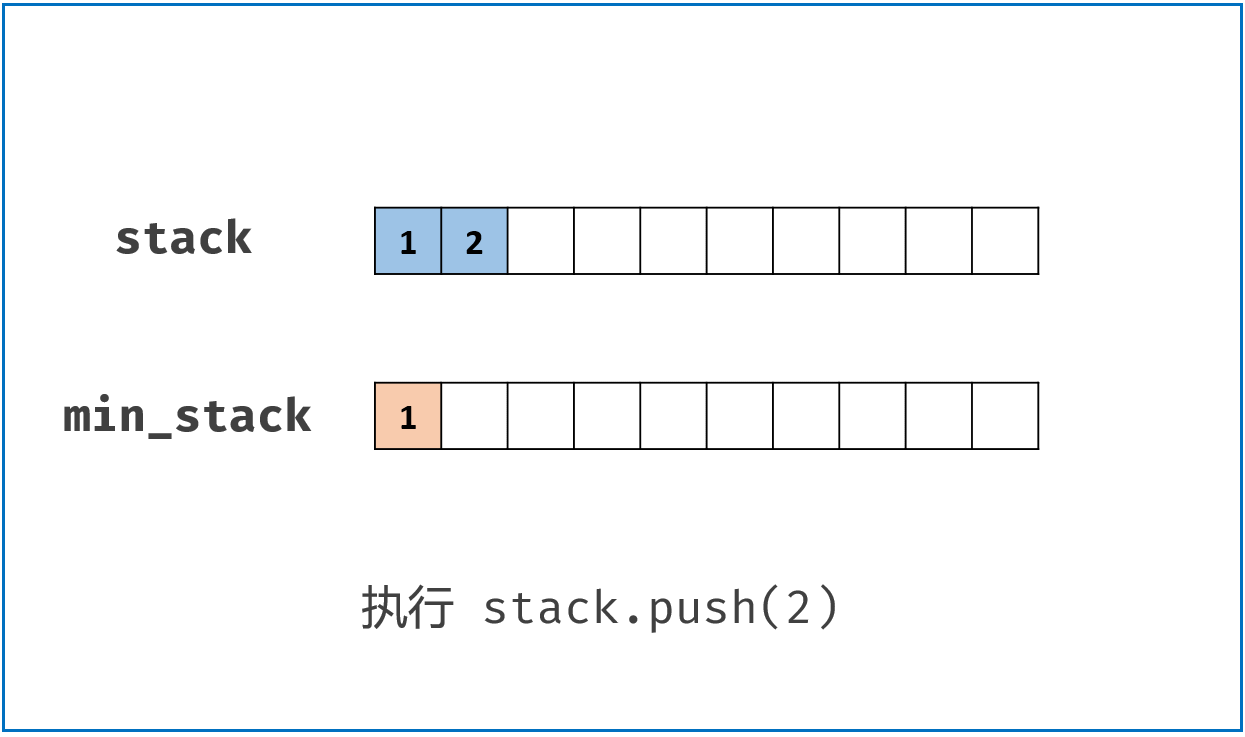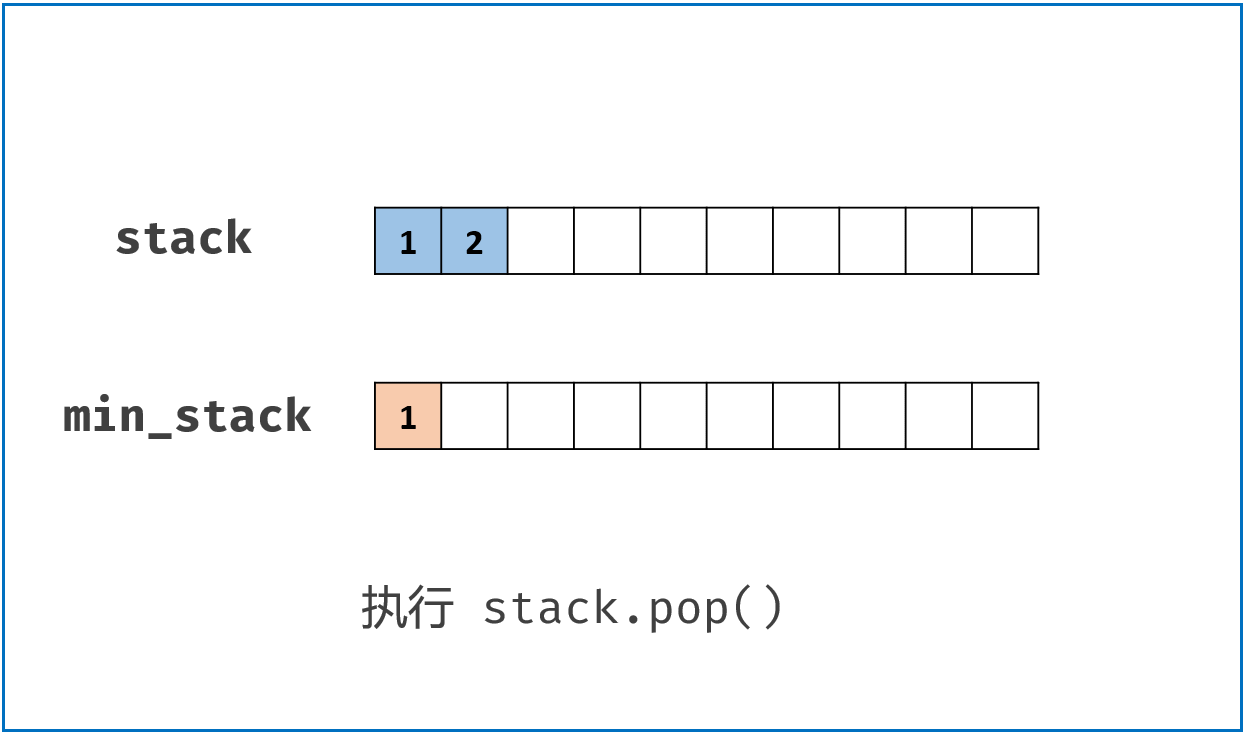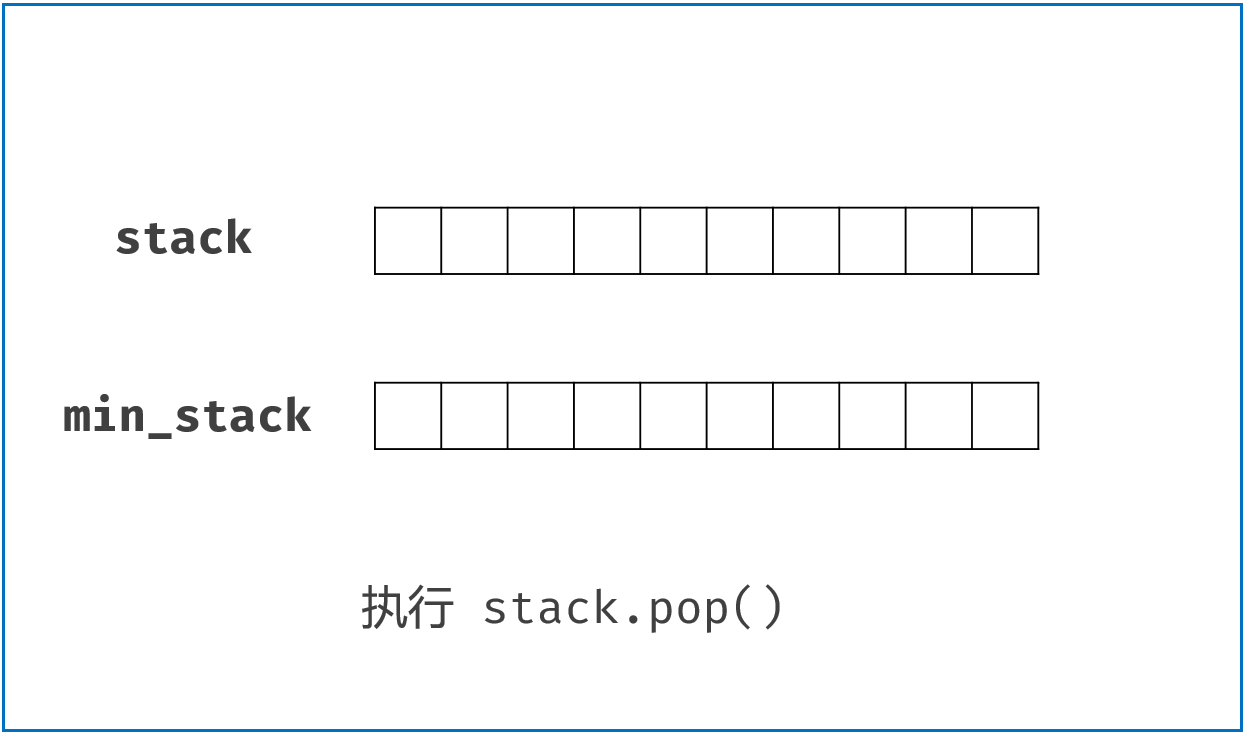
class MinStack:
def __init__(self):
self.stack = []
self.min_stack = []
def push(self, x: int) -> None:
self.stack.append(x)
if not self.min_stack or x <= self.min_stack[-1]:
self.min_stack.append(x)
def pop(self) -> None:
if self.stack.pop() == self.min_stack[-1]:
self.min_stack.pop()
def top(self) -> int:
return self.stack[-1]
def getMin(self) -> int:
return self.min_stack[-1]时间复杂度 O(1) :压栈,出栈,获取最小值的时间复杂度都为 O(1) 空间复杂度 O(N) :包含 N 个元素辅助栈占用线性大小的额外空间