LeetCode day21
Diffculty: Medium
116. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node
Topic: Tree, DFS
You are given a perfect binary tree where all leaves are on the same level, and every parent has two children. The binary tree has the following definition:
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
Follow up:
- You may only use constant extra space.
- Recursive approach is fine, you may assume implicit stack space does not count as extra space for this problem.
Example 1:
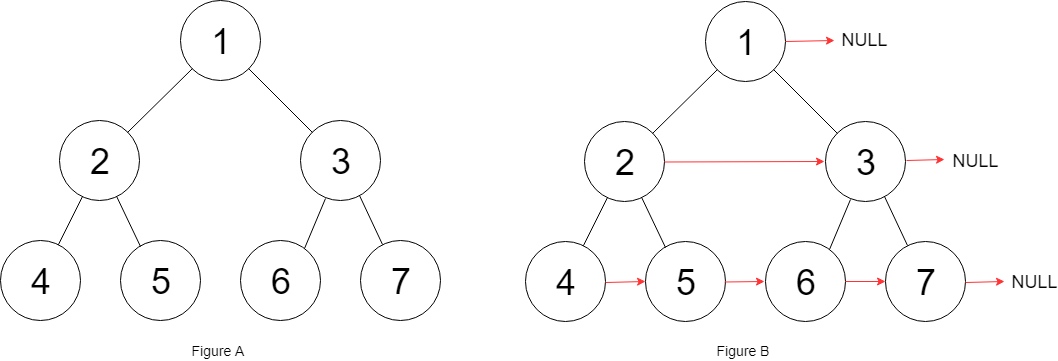
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [1,#,2,3,#,4,5,6,7,#]
Explanation: Given the above perfect binary tree (Figure A), your function should populate each next pointer to point to its next right node, just like in Figure B. The serialized output is in level order as connected by the next pointers, with '#' signifying the end of each level.Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the given tree is less than 4096.
- -1000 <= node.val <= 1000
Approach1
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val: int = 0, left: 'Node' = None, right: 'Node' = None, next: 'Node' = None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
self.next = next
"""
def connect(root: 'Node') -> 'Node':
if not root: return root
queue = deque()
queue.appendleft(root)
while queue:
p = None
n = len(queue)
for _ in range(n):
tmp = queue.pop()
if p:
p.next = tmp
p = p.next
else:
p = tmp
if tmp.left and tmp.right:
queue.appendleft(tmp.left)
queue.appendleft(tmp.right)
p.next = None
return rootApproach2
def connect(root: 'Node') -> 'Node':
if not root:
return
if root.left:
root.left.next = root.right
if root.next:
root.right.next = root.next.left
self.connect(root.left)
self.connect(root.right)
return root
def connect(root: 'Node') -> 'Node':
pre = root
while pre:
cur = pre
while cur:
if cur.left: cur.left.next = cur.right
if cur.right and cur.next: cur.right.next = cur.next.left
cur = cur.next
pre = pre.left
return root127. Word Ladder
Topic:BFS
Given two words (beginWord and endWord), and a dictionary’s word list, find the length of shortest transformation sequence from beginWord to endWord, such that:
- Only one letter can be changed at a time.
- Each transformed word must exist in the word list.
Note:
- Return 0 if there is no such transformation sequence.
- All words have the same length.
- All words contain only lowercase alphabetic characters.
- You may assume no duplicates in the word list.
- You may assume beginWord and endWord are non-empty and are not the same.
Example 1:
Input:
beginWord = "hit",
endWord = "cog",
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log","cog"]
Output: 5
Explanation: As one shortest transformation is "hit" -> "hot" -> "dot" -> "dog" -> "cog",
return its length 5.Example 2:
Input:
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
Output: 0
Explanation: The endWord "cog" is not in wordList, therefore no possible transformation.Approach1
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log","cog"]
from _collections import defaultdict,deque
def ladderLength(beginWord, endWord, wordList):
size, general_dic = len(beginWord), defaultdict(list)
for w in wordList:
for _ in range(size):
general_dic[w[:_]+"*"+w[_+1:]].append(w)
# print(general_dic)
# defaultdict(<class 'list'>, {'*ot': ['hot', 'dot', 'lot'], 'h*t': ['hot'], 'ho*': ['hot'], 'd*t': ['dot'], 'do*': ['dot', 'dog'], '*og': ['dog', 'log', 'cog'], 'd*g': ['dog'], 'l*t': ['lot'], 'lo*': ['lot', 'log'], 'l*g': ['log'], 'c*g': ['cog'], 'co*': ['cog']})
queue = deque()
queue.append((beginWord, 1)) # 因为在BFS中,queue中通常会同时混合多层的node,这就无法区分层了,要区分层就要queue中直接加入当前node所属层数。
mark_dic = defaultdict(bool) # bool 的默认值是false,因此所有不在list里的是false
mark_dic[beginWord] = True
print(queue) # deque([('hit', 1)])
print(mark_dic) # defaultdict(<class 'bool'>, {'hit': True})
while queue:
node, level = queue.popleft()
for i in range(size):
for neighbour in general_dic[node[:i]+'*'+node[i+1:]]:
# print(neighbour) # neightbot is the value in general_dict
if neighbour == endWord:
return level + 1
if not mark_dic[neighbour]:
mark_dic[neighbour] = True
queue.append((neighbour,level+1))
print('='*20)
return 0
print(ladderLength(beginWord,endWord,wordList))Approach2
slow
def ladderLength(beginWord, endWord, wordList):
if endWord not in wordList:
return 0
queue = deque()
queue.appendleft(beginWord)
word_len = len(beginWord)
res = 1
while queue:
n = len(queue)
for _ in range(n):
tmp = queue.pop()
if tmp == endWord:
return res
if tmp in wordList:
wordList.remove(tmp)
for i in range(word_len):
for a in range(97,123):
w = tmp[:i]+chr(a)+tmp[i+1:]
# print(w)
if w in wordList:
queue.appendleft(w)
res += 1
return 0Approach3
fastest, beginWord找endWord,endWord找beginWord
def ladderLength(beginWord, endWord, wordList):
if endWord not in wordList:
return 0
s1 = {beginWord}
s2 = {endWord}
n = len(beginWord)
step = 0
wordList.remove(endWord)
while s1 and s2:
step += 1
if len(s1) > len(s2):
s1,s2 = s2,s1
s = set()
for word in s1:
nextword = [word[:i] + chr(j) + word[i + 1:] for j in range(97, 123) for i in range(n)]
for w in nextword:
if w in s2:
return step+1
if w not in wordList:
continue
wordList.remove(w)
s.add(w)
s1 = s
return 0130. Surrounded Regions
Topic: Union Find, BFS, DFS
Given a 2D board containing ‘X’ and ‘O’ (the letter O), capture all regions surrounded by ‘X’.
A region is captured by flipping all ‘O’s into ‘X’s in that surrounded region.
Example:
X X X X
X O O X
X X O X
X O X XAfter running your function, the board should be:
X X X X
X X X X
X X X X
X O X XExplanation:
Surrounded regions shouldn’t be on the border, which means that any ‘O’ on the border of the board are not flipped to ‘X’. Any ‘O’ that is not on the border and it is not connected to an ‘O’ on the border will be flipped to ‘X’. Two cells are connected if they are adjacent cells connected horizontally or vertically.
Approach1
创建一个与board纬度一样parent列表来存储每个节点的父节点,每个’O’位置的父节点初始化为自己的索引,每个’X’位置的父节点初始化为[-1,-1]
创建一个与board纬度一样rank列表来存储每个节点的父节点的高度,用来做路径压缩,初始值均为0
- 定义find函数,用来返回当前节点的根节点
- 定义union函数,用来合并两个输入节点
- 定义union_find函数来做遍历board,两两合并节点
合并节点之后,遍历board的最外层,如果遍历到’O’,就把当前这个’O’的根节点的父节点设为[-1, -1]。一圈操作下来之后,board中根节点不是[-1, -1]的节点就是被’X’围住的’O’区域
def solve(board: List[List[str]]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
"""
if not board:
return
if not board[0]:
return
parent = [[[j, i] if board[j][i] == 'O' else [-1, -1] for i in range(len(board[0]))] for j in range(len(board))]
rank = [[0 for i in range(len(board[0]))] for j in range(len(board))]
def find(i, j):
if parent[i][j] == [-1, -1]:
return [-1, -1]
if parent[i][j] == [i, j]:
return [i, j]
else:
return find(parent[i][j][0], parent[i][j][1])
def union(x, y, m, n):
xyroot = find(x, y)
mnroot = find(m, n)
if board[x][y] != 'O' or board[m][n] != 'O':
return
if xyroot != mnroot:
if rank[xyroot[0]][xyroot[1]] > rank[mnroot[0]][mnroot[1]]:
parent[mnroot[0]][mnroot[1]] = [xyroot[0], xyroot[1]]
elif rank[xyroot[0]][xyroot[1]] < rank[mnroot[0]][mnroot[1]]:
parent[xyroot[0]][xyroot[1]] = [mnroot[0], mnroot[1]]
else:
parent[xyroot[0]][xyroot[1]] = [mnroot[0], mnroot[1]]
rank[mnroot[0]][mnroot[1]] += 1
def not_X(matricx):
for i in matricx:
if 'X' in i:
return True
return False
def union_find():
if not not_X(board):
return
for i in range(len(board)):
for j in range(len(board[0])):
if i == len(board)-1 and j == len(board[0])-1:
break
if i == len(board)-1:
union(i, j, i, j+1)
continue
if j == len(board[0])-1:
union(i, j, i+1, j)
continue
else:
union(i, j, i, j+1)
union(i, j, i+1, j)
for i in range(len(board)):
if board[i][0] == 'O':
this_root = find(i, 0)
parent[this_root[0]][this_root[1]] = [-1, -1]
if board[i][-1] == 'O':
this_root = find(i, len(board[0])-1)
parent[this_root[0]][this_root[1]] = [-1, -1]
for j in range(len(board[0])):
if board[0][j] == 'O':
this_root = find(0, j)
parent[this_root[0]][this_root[1]] = [-1, -1]
if board[-1][j] == 'O':
this_root = find(len(board)-1, j)
parent[this_root[0]][this_root[1]] = [-1, -1]
for i in range(len(board)):
for j in range(len(board[0])):
if find(i, j) != [-1, -1]:
board[i][j] = 'X'
union_find()Approach2
把边界 ‘O’ 并且与它连通这些点分在一起, Union set
def solve(board: List[List[str]]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
"""
f = {}
def find(x): # 为了找到联通的根节点
f.setdefault(x, x)
if f[x] != x:
f[x] = find(f[x])
return f[x]
def union(x, y):
f[find(y)] = find(x)
if not board or not board[0]:
return
row = len(board)
col = len(board[0])
dummy = row * col
for i in range(row):
for j in range(col):
if board[i][j] == "O":
if i == 0 or i == row - 1 or j == 0 or j == col - 1:
union(i * col + j, dummy)
else:
for x, y in [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)]:
# 'O'的四个方向有'O'的话也联通的在一起
if board[i + x][j + y] == "O":
union(i * col + j, (i + x) * col + (j + y))
for i in range(row):
for j in range(col):
if find(dummy) == find(i * col + j): # 对比'O'的根节点
board[i][j] = "O"
else:
board[i][j] = "X"Approach3
DFS
def solve(board: List[List[str]]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
"""
if not board or not board[0]:
return
row = len(board)
col = len(board[0])
def dfs(i, j):
board[i][j] = "B"
for x, y in [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)]:
tmp_i = i + x
tmp_j = j + y
if 1 <= tmp_i < row and 1 <= tmp_j < col and board[tmp_i][tmp_j] == "O":
dfs(tmp_i, tmp_j)
for j in range(col):
# 第一行
if board[0][j] == "O":
dfs(0, j)
# 最后一行
if board[row - 1][j] == "O":
dfs(row - 1, j)
for i in range(row):
# 第一列
if board[i][0] == "O":
dfs(i, 0)
# 最后一列
if board[i][col-1] == "O":
dfs(i, col - 1)
for i in range(row):
for j in range(col):
# O 变成 X
if board[i][j] == "O":
board[i][j] = "X"
# B 变成 O
if board[i][j] == "B":
board[i][j] = "O"Approach4
BFS
def solve(board: List[List[str]]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
"""
if not board or not board[0]:
return
row = len(board)
col = len(board[0])
def bfs(i, j):
from collections import deque
queue = deque()
queue.appendleft((i, j))
while queue:
i, j = queue.pop()
if 0 <= i < row and 0 <= j < col and board[i][j] == "O":
board[i][j] = "B"
for x, y in [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)]:
queue.appendleft((i + x, j + y))
for j in range(col):
# 第一行
if board[0][j] == "O":
bfs(0, j)
# 最后一行
if board[row - 1][j] == "O":
bfs(row - 1, j)
for i in range(row):
if board[i][0] == "O":
bfs(i, 0)
if board[i][col - 1] == "O":
bfs(i, col - 1)
for i in range(row):
for j in range(col):
if board[i][j] == "O":
board[i][j] = "X"
if board[i][j] == "B":
board[i][j] = "O"131. Palindrome Partitioning
Topic: Backtracking
Given a string s, partition s such that every substring of the partition is a palindrome.
Return all possible palindrome partitioning of s.
Example:
Input: "aab"
Output:
[
["aa","b"],
["a","a","b"]
]Approach1
def partition(s: str) -> List[List[str]]:
res = []
def helper(s, tmp):
if not s:
res.append(tmp)
for i in range(1, len(s) + 1):
if s[:i] == s[:i][::-1]:
helper(s[i:], tmp + [s[:i]])
helper(s, [])
return resApproach2
DP
def partition(s: str) -> List[List[str]]:
n = len(s)
dp = [[False] * n for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
for j in range(i + 1):
if (s[i] == s[j]) and (i - j <= 2 or dp[j + 1][i - 1]):
dp[j][i] = True
#print(dp)
res = []
def helper(i, tmp):
if i == n:
res.append(tmp)
for j in range(i, n):
if dp[i][j]:
helper(j + 1, tmp + [s[i: j + 1]])
helper(0, [])
return res